Timing Belt vs. Timing Chain: What's the Difference?
This listicle clarifies the key differences between a timing belt and a timing chain. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for proper vehicle maintenance and can prevent costly engine damage. Learn about these components, plus related parts like the timing chain tensioner, timing gears, variable valve timing (VVT) actuators, and cam phasers. Knowing whether your car has a timing belt or timing chain, and when it needs service, will help you keep your engine running smoothly and avoid unexpected breakdowns.
1. Timing Belt
When discussing engine timing, the critical component responsible for synchronization is often either a timing belt or a timing chain. A timing belt (also known as a cambelt) is a reinforced rubber belt with teeth that precisely engage with sprockets on the crankshaft and camshaft(s). This synchronization is crucial for proper engine operation, ensuring the valves open and close at the correct moments during the intake and exhaust strokes of each cylinder. The belt's location outside the engine block, connecting various pulleys and tensioners, makes it a vital yet vulnerable part of the engine system.
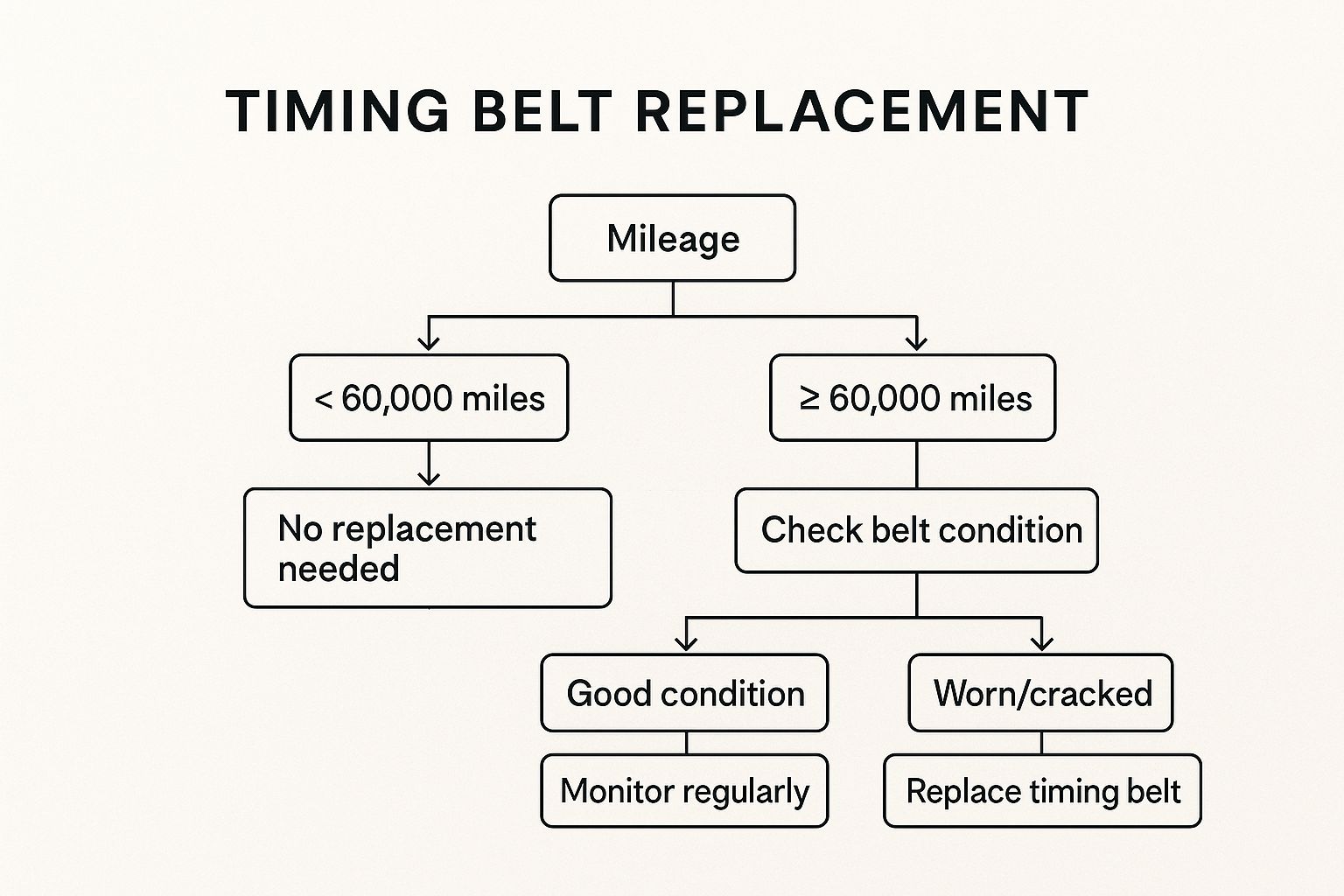
The infographic above provides a decision tree to help determine whether a vehicle uses a timing belt or chain. This is crucial information for maintenance scheduling. By starting with the vehicle's make, model, and engine, you can follow the branches to determine the type of timing mechanism used. For Fort Worth drivers, knowing this information can help avoid costly repairs by ensuring timely replacement of the timing belt.
Timing belts are typically quieter than chains and require less lubrication due to their external placement. Their lightweight design contributes to better fuel efficiency and reduced overall engine weight. Examples of vehicles commonly using timing belts include Honda K-series engines (Civic, Accord), Toyota's 3MZ-FE V6 (Camry, Highlander), Subaru's EJ series (Impreza, Legacy), Volkswagen's EA888, and Ford's Zetec engines. This widespread use highlights the timing belt's importance in the automotive industry. Leaders in timing belt manufacturing and implementation include Gates Corporation, Continental AG, Dayco, Toyota, and Honda, further solidifying the technology's significance.
While timing belts offer advantages like quiet operation and lower manufacturing costs, they have limitations. Their lifespan typically ranges from 60,000 to 100,000 miles, requiring periodic replacement. A broken timing belt can lead to catastrophic engine damage, making adherence to the manufacturer's recommended replacement schedule vital. Furthermore, belts are more susceptible to damage from environmental factors like heat, oil, and debris. For budget-conscious drivers in Fort Worth, the lower initial cost of a timing belt engine can be offset by the higher long-term maintenance costs associated with replacements.
For owners of high-mileage or aging vehicles in Fort Worth, understanding the condition of the timing belt is especially critical. When purchasing a used car, always inquire about the timing belt's service history. Unusual noises from the engine could indicate belt wear and should be addressed promptly by a qualified mechanic. Proactive maintenance, including replacing the water pump and tensioners during a belt change, can help mitigate potential issues.
The decision tree clearly highlights the importance of knowing your vehicle's specifications. A broken timing belt can lead to significant engine damage, emphasizing the importance of preventative maintenance. For Fort Worth drivers, understanding this key difference between timing belts and chains is crucial for proper vehicle care and budgeting for potential repairs. This makes the timing belt an essential consideration when comparing timing mechanisms.
2. Timing Chain
When considering "timing belt or timing chain" for your vehicle, understanding the distinctions is crucial. A timing chain is a robust metal chain, resembling a heavy-duty bicycle chain, responsible for synchronizing the rotation of the crankshaft and camshaft(s). This synchronization is vital for ensuring precise valve timing, which dictates when the engine's valves open and close to allow for the intake of air and fuel and the exhaust of combustion gases. This precise timing is essential for optimal engine performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions control. Unlike a timing belt, which is typically made of rubber and requires periodic replacement, a timing chain is designed to endure the lifespan of the engine, operating internally and lubricated by the engine's oil. This internal placement and constant lubrication contribute to its longevity. A tensioner system keeps the chain taut, preventing slippage and maintaining accurate timing.
Timing chains offer a compelling alternative to timing belts due to their inherent durability and longevity. This makes them a popular choice for high-performance engines, higher displacement engines, and many modern vehicles. Examples of engines utilizing timing chains include BMW's N52 inline-six engines found in their 3, 5, and X Series vehicles, the potent GM LS V8 engine family powering Corvettes, Camaros, and trucks, and the sophisticated Mercedes-Benz M276 V6 engines in their E-Class and S-Class models. Other notable examples include the legendary Toyota 2JZ-GTE engine from the Supra and Ford's robust Coyote V8 found in the Mustang and F-150. These examples demonstrate the widespread adoption of timing chains across a range of vehicle types and performance levels.
Features and Benefits:
- Metal construction: Provides superior durability and resistance to wear and tear compared to rubber timing belts.
- Internal operation and oil lubrication: Ensures consistent lubrication and protection from external elements, contributing to extended lifespan.
- Long lifespan: Typically designed to last the lifetime of the engine (150,000+ miles), eliminating the need for scheduled replacements.
- High-temperature and oil resistance: Able to withstand the harsh conditions within the engine compartment.
- Handles higher loads and stresses: Suitable for high-performance and larger displacement engines.
Pros:
- Superior durability compared to timing belts
- Longer lifespan (typically 150,000+ miles)
- Reduced maintenance (no scheduled replacements)
- Better resistance to heat and oil
- Handles greater engine stresses
Cons:
- Noisier operation than timing belts
- Adds weight to the engine
- Higher replacement cost (if needed)
- Potential for stretching and the need for adjustments
- More complex and costly repairs
Tips for Timing Chain Maintenance:
- Oil Changes: Use high-quality engine oil and adhere to the manufacturer's recommended oil change intervals. Proper lubrication is critical for timing chain longevity.
- Listen for unusual sounds: Be attentive to any rattling or slapping sounds coming from the engine, as these could indicate chain wear or tensioner issues.
- Address oil pressure problems: Low oil pressure can starve the timing chain of lubrication, leading to premature wear or damage. Address any oil pressure issues promptly.
- Consider preventative replacement (high mileage): For vehicles with exceptionally high mileage (150,000+ miles), preventative chain replacement might be a worthwhile consideration.
- Use quality parts: When replacing a timing chain, always use OEM or equivalent quality parts to ensure proper fit and performance.
A timing chain is a critical component deserving of its place on this list because it represents a durable and reliable solution for valve timing. While it may have some drawbacks, such as increased noise and complexity, the benefits of extended lifespan and reduced maintenance often outweigh the negatives, particularly for drivers in Fort Worth seeking long-term reliability and cost-effectiveness. For those with high-mileage vehicles or performance-oriented engines, the robust nature of a timing chain provides peace of mind and minimizes the risk of unexpected timing belt failures.
3. Timing Chain Tensioner: A Critical Component in Timing Chain Systems
When deciding between a timing belt or timing chain, understanding the supporting components of a timing chain system is essential. A key player in that system is the timing chain tensioner. This vital component ensures the timing chain remains taut, preventing slack that can lead to performance issues or even catastrophic engine damage. It's a crucial element for anyone considering a vehicle with a timing chain, especially for car owners in Fort Worth seeking reliable maintenance for their vehicles, whether it's a high-mileage car, a fleet vehicle, or simply one they rely on for daily commutes.
The timing chain tensioner constantly applies the correct amount of pressure to the timing chain, keeping it properly engaged with the crankshaft and camshaft sprockets. This precise control is crucial for maintaining accurate valve timing, which directly impacts engine performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions. Without a properly functioning tensioner, the chain can become loose, leading to rattling noises, poor engine performance, and potentially the chain skipping teeth on the sprockets. Such a scenario can result in severe engine damage, requiring costly repairs.
Modern timing chain tensioners are typically designed as either hydraulic or mechanical spring-loaded devices. Hydraulic tensioners utilize engine oil pressure to maintain tension, while mechanical tensioners rely on spring force. Both types automatically adjust to compensate for chain stretch as the engine ages. They often include features like a ratcheting mechanism to prevent the chain from backsliding and a guide rail or shoe to further control chain movement.
Pros of a Well-Functioning Timing Chain Tensioner:
- Prevents Timing Chain Slack: Keeps the chain taut, preventing skipping and potential engine damage. This is crucial for budget-conscious drivers in Fort Worth who want to avoid expensive repairs.
- Reduces Noise: Minimizes chain rattle, especially during cold starts, providing a quieter and smoother engine operation.
- Extends Timing Chain Life: Controlled chain movement reduces wear and tear, maximizing the lifespan of the timing chain system.
- Maintains Precise Valve Timing: Ensures optimal engine performance, fuel efficiency, and lower emissions, important for both performance and safety-conscious drivers.
- Self-Adjusting: Automatically compensates for chain stretch, requiring less frequent maintenance.
Cons and Potential Issues:
- Potential Failure Points: Tensioners, particularly hydraulic ones, can fail due to low oil pressure, oil contamination, or component wear. This is why regular maintenance and using quality oil is vital for Fort Worth drivers.
- Plastic Components: Some tensioners incorporate plastic parts that can become brittle and break over time, especially in high-mileage engines.
- Catastrophic Failure: A failed tensioner can lead to significant engine damage, often requiring extensive and expensive repairs.
- Replacement Complexity: Replacing a tensioner often requires considerable disassembly of the engine.
Examples of Vehicles and Tensioner Designs:
Several vehicle models are known for specific timing chain tensioner designs, both good and bad. Some examples include Volkswagen/Audi 2.0T TSI engines with known tensioner issues, BMW N20/N26 engines with updated tensioner designs, and GM LS series engines known for reliable tensioners. Understanding the specific design in your vehicle can help you be proactive in maintenance and avoid potential problems.
Tips for Maintaining Timing Chain Tensioners:
- Monitor for Unusual Noise: Pay attention to any unusual rattling or whining noises from the engine, especially during cold starts.
- Regular Oil Changes: Maintain proper oil pressure and use high-quality oil to ensure hydraulic tensioners function correctly. This is crucial for all Fort Worth drivers, but especially for those with high-mileage or aging vehicles.
- Preventative Replacement: Consider replacing the tensioner, especially in high-mileage engines, when performing other timing chain related services to prevent unexpected failures.
- Check for Updates: For vehicles with known tensioner problems, research and inquire about updated or revised tensioner designs that may offer improved reliability. This is especially helpful for fleet managers and small business owners in Fort Worth who rely on dependable service.
The timing chain tensioner is a small but vital component in the timing chain system. Understanding its function, potential issues, and maintenance requirements is crucial for any vehicle owner, especially those looking for convenient, reliable, and cost-effective maintenance in Fort Worth. By following these tips and being proactive with maintenance, you can help ensure your engine runs smoothly and avoid costly repairs down the road.
4. Timing Gears
When deciding between a timing belt or timing chain, timing gears represent a less common, but incredibly durable, alternative. This method uses metal gears to directly connect the crankshaft to the camshaft(s), precisely synchronizing valve timing with piston movement. Unlike belts or chains, timing gears offer a direct mechanical connection with no elasticity or potential for stretching, making them a robust choice for specific applications.
Timing gears are typically crafted from hardened steel or iron, and occasionally from composite materials. This inherent strength makes them exceptionally long-lasting, often outlasting the engine itself. The direct gear-to-gear connection eliminates the need for tension adjustments or replacements that are common with belts and chains. This direct drive also translates to precise timing with minimal variation over time, contributing to consistent engine performance.
How Timing Gears Work:
The crankshaft, responsible for converting the engine's reciprocating motion into rotational power, directly drives the camshaft(s) via the timing gears. The camshaft(s) then control the opening and closing of the engine's valves, allowing the intake and exhaust of gases at precise moments. The gear teeth are often helical cut. This design feature reduces noise and ensures smoother, more efficient engagement between the gears.
Why Choose Timing Gears?
Timing gears are ideal for applications where durability and longevity are paramount. This includes heavy-duty applications like commercial trucks and industrial equipment, as well as some high-performance engines where absolute reliability is essential. They are also frequently found in older engines where this technology was more common.
Pros:
- Exceptional durability and longevity: Often outlasts the engine itself.
- Zero maintenance: No adjustments or replacements needed under normal operating conditions.
- No stretching or tension adjustments: Maintains precise timing over time.
- Precise timing with minimal variation: Contributes to consistent engine performance.
- Excellent for heavy-duty or commercial applications: Handles the stress of high-power and continuous operation.
Cons:
- Significantly heavier than belts or chains: Adds more weight to the engine.
- Noisier operation: Produces a characteristic "gear whine."
- More expensive to manufacture: Increased complexity compared to belts and chains.
- Creates more rotational mass and inertia: Can slightly reduce engine responsiveness.
- Repairs are complex and costly if damage occurs: Requires specialized tools and expertise.
Examples of Timing Gear Implementations:
- Classic Chevrolet inline-six engines
- Many diesel engines in commercial trucks (Cummins, Detroit Diesel)
- Older Land Rover engines
- Classic Jeep 4.0L inline-six engines (partially gear-driven)
- Certain racing applications requiring ultimate reliability
Tips for Maintaining Timing Gears:
- Ensure proper lubrication: Use high-quality engine oils as recommended by the manufacturer.
- Listen for changes in gear noise: Unusual noises may indicate wear or damage.
- During engine rebuilds: Inspect gear teeth for pitting, chipping, or excessive wear.
- Maintain proper backlash specifications during assembly: This ensures proper gear engagement and prevents premature wear.
- Note gear-to-gear timing marks: These marks are crucial for accurate reassembly and proper timing.
Popularized By:
Companies like Cummins, Caterpillar, Detroit Diesel, and International Harvester have long championed gear-driven designs, showcasing the robustness of this technology in demanding environments. The AMC/Jeep 4.0L inline-six engine also utilized a partially gear-driven valvetrain, highlighting its application in consumer vehicles.
Timing gears offer a distinct advantage in specific applications where extreme durability and consistent performance are required. While they might not be suitable for all vehicles due to added weight, noise, and cost, they represent a viable and robust alternative to timing belts or timing chains when choosing between a timing belt or timing chain.
5. Variable Valve Timing (VVT) Actuators
Variable Valve Timing (VVT) actuators are a crucial component of modern engines, playing a significant role in how your engine performs and interacts with its timing belt or timing chain. Understanding their function is essential for informed maintenance decisions, especially for owners of high-mileage or aging vehicles in Fort Worth seeking reliable and cost-effective service.
VVT actuators are sophisticated components that optimize engine performance and efficiency by dynamically adjusting valve timing based on operating conditions. They work in conjunction with the timing belt or timing chain system. The timing belt or chain connects the crankshaft to the camshaft(s), which control the opening and closing of the engine's valves. VVT actuators, typically mounted on the end of the camshaft, alter the camshaft's position relative to the crankshaft. This dynamic adjustment effectively advances or retards valve timing, allowing the engine to "breathe" more efficiently at different RPMs. This precise control is managed by the engine's computer (ECU), which constantly monitors factors like engine speed, load, and throttle position.
How VVT Improves Engine Performance
VVT systems offer several benefits, making them a valuable addition to modern engines:
- Improved Fuel Economy: Optimizing valve timing allows the engine to burn fuel more efficiently, resulting in better gas mileage. This is a key concern for budget-conscious drivers in Fort Worth.
- Increased Power Output: VVT expands the engine's power band, providing more torque at lower RPMs and greater horsepower at higher RPMs. This leads to improved acceleration and overall performance.
- Reduced Emissions: Enhanced combustion efficiency through VVT minimizes harmful exhaust gases, helping vehicles meet stricter emissions standards and contributing to a cleaner environment.
Types of VVT Actuators and Examples
VVT actuators are primarily hydraulic or electric. Hydraulic systems utilize oil pressure to adjust the camshaft timing, while electric actuators offer more precise control. Several manufacturers have implemented successful VVT systems:
- Toyota's VVT-i: A widely used hydraulic system known for its reliability and effectiveness.
- BMW's VANOS/Double VANOS: BMW's innovative system offers advanced timing adjustments for both intake and exhaust valves.
- Honda's VTEC: Honda's system is famous for its ability to switch between different camshaft profiles for optimal performance at various engine speeds.
- Ford's Ti-VCT: Ford's twin independent variable camshaft timing system provides precise control over both intake and exhaust valves.
- Nissan's CVTC: Nissan's continuously variable valve timing control system provides seamless adjustments for optimal performance.
Pros and Cons of VVT Systems
While VVT offers numerous advantages, it's essential to be aware of potential drawbacks:
Pros:
- Enhanced fuel economy
- Increased power and torque
- Reduced emissions
Cons:
- Added complexity to the timing system
- Potential for failure due to oil contamination or pressure issues (especially important for owners of aging vehicles)
- Higher replacement cost compared to traditional timing systems
- Possibility of oil leaks over time
Actionable Tips for Maintaining VVT Systems
For car owners in Fort Worth, maintaining a healthy VVT system is crucial for optimal engine performance and longevity. Here are some actionable tips:
- Use High-Quality Oil and Maintain Regular Oil Change Intervals: Clean oil is vital for proper hydraulic VVT actuator function.
- Address Check Engine Lights Promptly: Ignoring VVT-related codes can lead to more serious problems. Certified service in Fort Worth is recommended for accurate diagnostics and repairs.
- Listen for Rattling Noises: Unusual noises from the engine, especially during startup or acceleration, could indicate VVT actuator failure.
- Consider Preventative Maintenance: For known problematic VVT systems, preventative maintenance, including cleaning with specialized engine flushes, can prevent costly repairs down the line.
Why VVT Matters for Timing Belt or Timing Chain Maintenance
VVT actuators are integral to modern timing belt or timing chain systems. When replacing a timing belt or chain, it's crucial to ensure the VVT system is inspected and serviced if necessary. Ignoring potential VVT issues during timing belt/chain service can lead to decreased performance, reduced fuel economy, and potential engine damage. For drivers in Fort Worth, consulting with a qualified mechanic specializing in timing belt or chain replacement and VVT systems is essential for comprehensive and reliable service.
6. Cam Phasers
Cam phasers play a crucial role in modern engine performance, especially in vehicles utilizing a timing belt or timing chain. These components are integral to Variable Valve Timing (VVT) systems and allow for dynamic adjustments to the camshaft timing while the engine is running. This adjustability optimizes engine performance, emissions, and fuel economy across a wider range of operating conditions than would be possible with a fixed camshaft timing. By precisely altering when the engine's valves open and close, cam phasers ensure efficient combustion, whether you're accelerating onto the freeway or cruising through Fort Worth traffic.

Cam phasers achieve this dynamic control through internal helical splines or vanes that adjust the camshaft's rotational position relative to the timing chain sprocket or belt drive gear. The adjustment is typically actuated by oil pressure, regulated by solenoids controlled by the Engine Control Unit (ECU). This allows for continuous or staged adjustments to valve timing, reacting to your driving demands in real-time. This is particularly important for drivers in Fort Worth who experience varied driving conditions, from stop-and-go city traffic to open highway stretches.
Features and Benefits:
- Precise Valve Timing Control: Offers continuous or staged adjustment for optimized performance.
- Enhanced Efficiency: Improves combustion across all engine speeds, leading to better fuel economy, especially beneficial for budget-conscious drivers.
- Improved Power Delivery: Boosts low-end torque for responsive acceleration while maintaining high-end power for highway merging and passing.
- Reduced Emissions: Optimizes valve overlap to minimize harmful exhaust gases.
- Smoother Operation: Contributes to a smoother idle and improved drivability, particularly important for aging vehicles.
Pros and Cons:
Pros:
- Increased fuel efficiency, a major advantage for Fort Worth drivers.
- Improved engine performance across a wider RPM range.
- Reduced emissions, contributing to a cleaner environment.
- Enhanced drivability and smoother engine operation.
Cons:
- Susceptibility to failure due to oil sludge and contamination, highlighting the importance of regular maintenance.
- Increased mechanical complexity, potentially leading to higher repair costs.
- Can develop rattling noises when worn, requiring prompt attention to prevent further damage.
Examples of Cam Phaser Implementation:
Several manufacturers have successfully integrated cam phasers into their engines, including Ford (Triton and Coyote V8s), General Motors (EcoTec engines), Audi/VW (2.0T FSI and TSI engines), Dodge/Chrysler (Hemi engines with MDS), and Mazda (SkyActiv-G engines). These examples demonstrate the widespread adoption and effectiveness of this technology.
Actionable Tips for Car Owners:
- Regular Oil Changes: Adhere to manufacturer-recommended oil change intervals and use high-quality oil to prevent sludge buildup. This is especially crucial for vehicles with cam phasers.
- Address Rattling Noises: Don't ignore unusual engine noises, particularly rattling sounds, as they could indicate a problem with the cam phasers. Prompt diagnosis and repair can prevent more extensive and costly damage.
- Preventative Maintenance: Consider periodic engine oil flushes to remove contaminants and maintain optimal oil cleanliness.
- Quality Replacements: When replacing cam phasers, opt for OEM or high-quality aftermarket parts to ensure proper function and longevity. For high-mileage vehicles in Fort Worth, this is particularly important to maintain reliability.
Cam phasers are a critical component in modern engines equipped with a timing belt or timing chain. While they offer significant benefits in performance, efficiency, and emissions, they require proper maintenance to ensure reliable operation. By following the tips outlined above, Fort Worth drivers can maximize the lifespan and benefits of their vehicle's cam phasers. If you suspect any issues with your cam phasers, consult a qualified mechanic for diagnosis and repair.
6-Part Timing System Comparison
| Component | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes ⭐📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Timing Belt | Moderate: requires periodic replacement and tensioner changes | Moderate: less costly material but needs regular maintenance | Reliable valve timing, quieter operation, energy efficient | Everyday passenger vehicles, lightweight engines | Quiet, lightweight, cost-effective |
| Timing Chain | High: installed inside engine, requires oil maintenance | Higher: durable metal chain, needs quality engine oil | Long-lasting timing synchronization, minimal replacement | Performance and heavy-duty engines | Durable, low maintenance, high-temperature resistant |
| Timing Chain Tensioner | Moderate to High: complex hydraulic/mechanical device | Moderate: requires quality oil and periodic inspection | Maintains proper chain tension, reduces noise, prevents failures | Engines with timing chains requiring tension control | Automatic adjustment, extends chain life |
| Timing Gears | High: precise machining and alignment critical | High: heavy metal parts, complex assembly | Extremely durable, no stretching, precise timing | Heavy-duty, commercial, classic engines | Maintenance-free, long-lasting, precise timing |
| Variable Valve Timing Actuators | High: integrated computer-controlled hydraulic/electric systems | High: requires quality oil, ECU control, intricate design | Improved fuel economy, power, emissions reduction | Modern engines emphasizing performance and efficiency | Optimizes valve timing dynamically |
| Cam Phasers | High: hydraulic actuators with solenoid control | High: requires clean oil, ECU control, specialized parts | Continuous camshaft timing adjustment, smoother performance | Engines with VVT systems needing fine timing control | Enhances torque, reduces emissions, better drivability |
Keep Your Engine in Top Shape
Understanding the difference between a timing belt or timing chain, along with the related components like the timing chain tensioner, timing gears, variable valve timing (VVT) actuators, and cam phasers, is crucial for maintaining your vehicle's engine health. We've explored each of these elements, highlighting the importance of their roles and the potential consequences of neglecting their maintenance. The key takeaway? Whether your engine utilizes a timing belt or a timing chain, proactive maintenance is essential to prevent costly and inconvenient breakdowns. Regular maintenance is essential for both timing belts and timing chains. For expert preventative auto repair and to keep your engine in top shape, consult the Car Maintenance Schedule by Mileage: Keep Your Car in Top Shape from Kwik Kar of Mesquite. By understanding these components and their maintenance needs, you're not just extending the life of your engine, you're ensuring reliable performance, saving money in the long run, and prioritizing your safety on the road.
Mastering these concepts empowers you to make informed decisions about your vehicle's care, which translates to a smoother, safer, and more cost-effective driving experience. Don't wait for a problem to arise – be proactive! For expert advice and service on your timing belt or timing chain, visit Kwik Kar Oil Change and Auto Care. Our ASE-certified technicians in Fort Worth can diagnose and address any timing-related issues, ensuring your engine stays in top condition and helping you avoid costly repairs down the line.



